Artificial intelligence (AI) models have rapidly advanced, enabling generative systems like ChatGPT and GPT-4 to produce remarkably human-like text, images, and code. Yet, beneath this progress lies a critical and emerging risk known as AI model collapse — a phenomenon where large language models (LLMs) begin to degrade over time, producing incoherent, biased, or meaningless outputs due to recursive reliance on AI-generated data.
This article examines what AI model collapse is, why it matters, and how developers, researchers, and enterprises can mitigate this growing risk through better data governance, model oversight, and intelligent training strategies.
What Is AI Model Collapse?
AI model collapse refers to the progressive degradation of an AI model’s performance caused by training on data that has been generated by other AI systems rather than original, human-generated content. Over time, this recursive process leads to a loss of data diversity, accuracy, and meaning.
When a new model is trained primarily or partially on AI-generated data — such as text or images produced by previous LLMs — it inherits the biases, errors, and distortions embedded in those outputs. As this pattern continues over multiple generations of model training, the distribution of training data drifts away from real-world information, causing outputs to become less coherent and eventually collapse into gibberish or repetitive, low-value text.
The concept of model collapse was formally explored in the 2023 paper “The Curse of Recursion: Training on Generated Data Makes Models Forget” by Ilia Shumailov, Zakhar Shumaylov, and Yiren Zhao. Their research demonstrated that when generative AI models — including variational autoencoders (VAEs) and diffusion models — are trained recursively on synthetic data, they experience compounding information loss and entropy increase, leading to catastrophic degradation of quality.
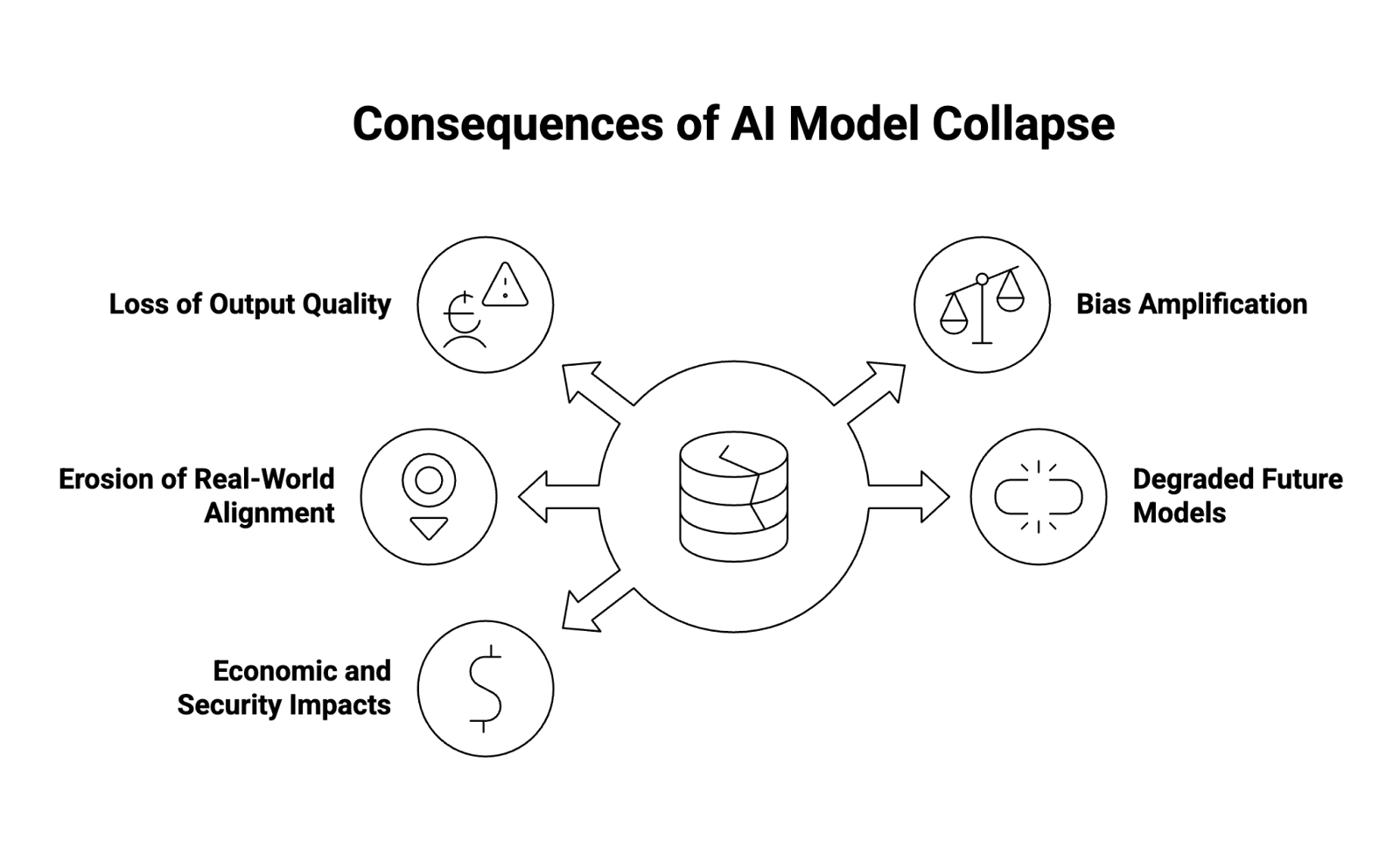
What Are the Consequences of Model Collapse?
The consequences of AI model collapse ripple across the AI ecosystem, affecting not only technical model performance but also business reliability, trust, and the integrity of future AI systems.
1. Loss of Output Quality
As models absorb increasing amounts of synthetic or low-quality data, their ability to produce accurate, coherent, or creative text diminishes. This manifests as nonsensical sentences, factual inaccuracies, or repetitive phrasing — symptoms often described as semantic drift or output entropy.
2. Bias Amplification
Because AI-generated content often mirrors the biases and limitations of its source models, recursive training can reinforce existing distortions in data — from gender or racial bias to ideological skew — compounding societal and ethical risks.
3. Erosion of Real-World Alignment
AI systems trained primarily on AI outputs lose grounding in real-world data. This disconnect weakens the model’s ability to reason about current events, cultural context, and factual accuracy, making it less aligned with human expectations and truth.
4. Degraded Future Generations of Models
Model collapse doesn’t just affect a single system — it threatens the next generation of foundation models. As more models trained on synthetic data are used to generate new datasets, the entire AI ecosystem risks an information feedback loop, leading to systemic degradation across the industry.
5. Economic and Security Impacts
In industries like healthcare, finance, or cybersecurity, degraded model performance could lead to dangerous or costly decisions. Misdiagnosed conditions, inaccurate risk assessments, or false anomaly detections may result if AI models lose connection to reliable, human-validated data.
What Causes AI Model Collapse During Training?
AI model collapse stems from how training datasets evolve over time. In the early stages of AI development, models like GPT-2, GPT-3, and BERT were trained on vast corpora of human-generated data — news articles, books, research papers, and web content. However, as AI content generation scales exponentially, much of the new data being published online originates from generative AI models themselves.
When new LLMs or machine learning models use this contaminated data for training, they inadvertently learn from degraded signals. Over multiple training cycles, recursively generated data causes statistical distortions known as data distribution drift.
Key causes include:
- Recursive data training — repeatedly feeding AI-generated content into new models.
- Reduced access to original data — declining volume of publicly available, high-quality human-authored data.
- Synthetic data contamination — inclusion of unverified or low-fidelity synthetic datasets without proper labeling.
- Feedback loops in data aggregation — automated scraping of web content that already includes large portions of GenAI text.
- Lack of provenance tracking — inability to trace which data points are AI-generated versus human-written.
The outcome is an entropy spiral, where small errors compound, ultimately leading models to produce incoherent, repetitive, or incorrect outputs — the hallmark of model collapse.
What Are the Signs of AI Model Collapse?
Identifying early warning signs is crucial for preventing model collapse before it renders an AI system unusable. Some observable indicators include:
- Decreased diversity of outputs — Responses become increasingly similar across prompts, reflecting over-compression of information.
- Higher factual inaccuracy — Increased rate of hallucinations or false claims.
- Unnatural phrasing or grammar — Outputs may include awkward or repetitive structures not found in natural language.
- Loss of novelty — Models fail to generate new ideas, instead recycling fragments of older outputs.
- Reduced correlation to training objectives — The model’s predictions or generations deviate from expected results during validation.
- Entropy increase in latent representations — Observed in technical model metrics when latent space becomes saturated or uninformative.
In production environments, these signs can appear as declining user satisfaction, higher error rates, or unpredictable model behavior across AI applications and APIs.
Is AI Model Collapse Inevitable?
While model collapse is a significant risk, it is not inevitable — but it does require active mitigation. The challenge is not that AI models inherently degrade, but that AI development pipelines often lack visibility into the origin and quality of training data.
If future models rely too heavily on AI-generated content without robust provenance control or validation mechanisms, collapse becomes increasingly likely. However, with proper data curation, oversight, and governance, LLMs can maintain high performance across generations.
Research from OpenAI and independent teams (including work by Papernot et al.) has emphasized the importance of maintaining original data diversity and data lineage tracking to prevent systemic degradation across machine learning models.
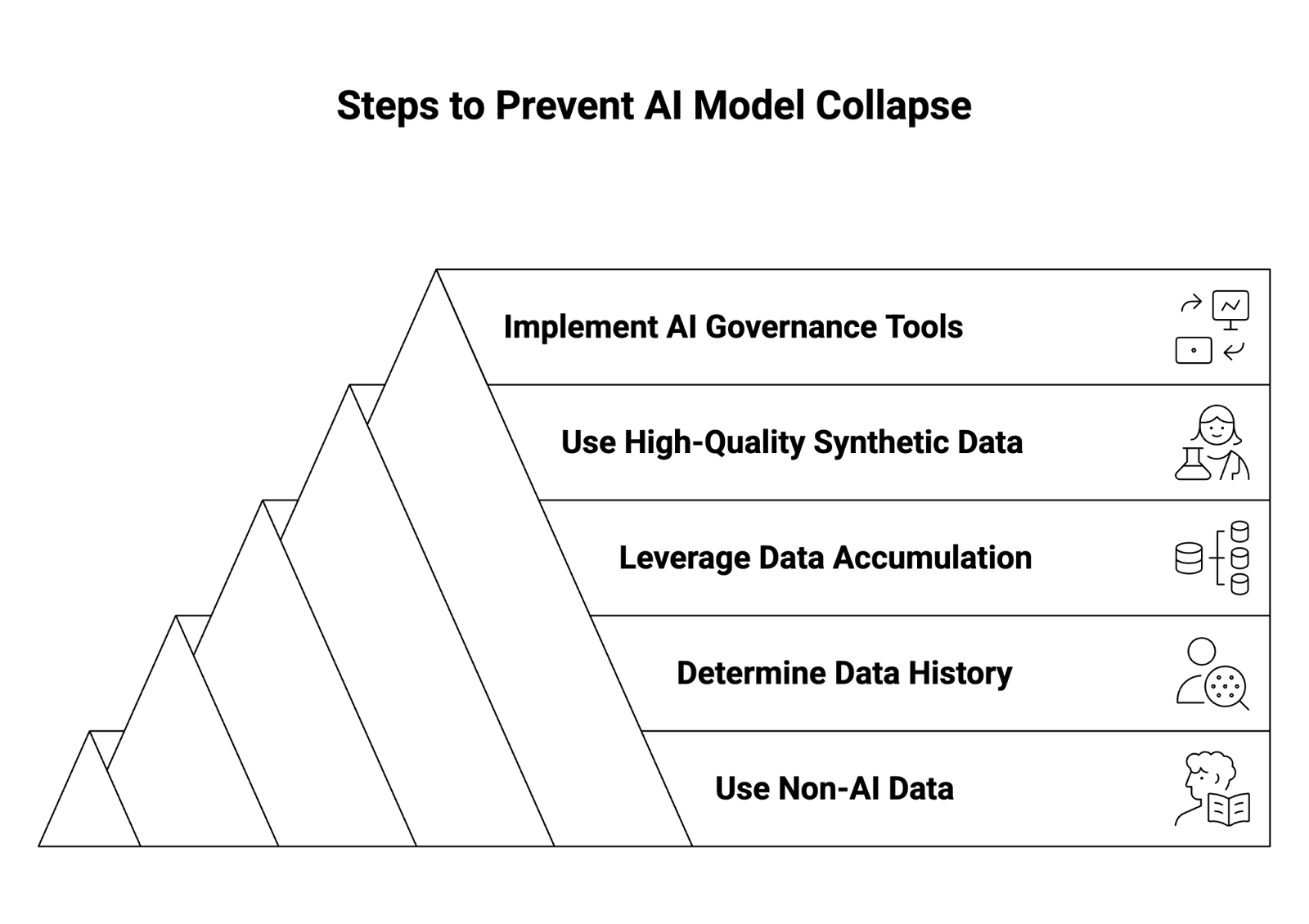
How Can You Prevent AI Model Collapse?
Preventing model collapse requires a multi-layered data management and governance strategy that prioritizes diversity, transparency, and ongoing validation. Below are key practices that AI developers and enterprises can adopt.
1. Use Non-AI Data Sources
Prioritize human-generated data wherever possible. Curate datasets from verified, real-world sources such as academic publications, government archives, and peer-reviewed content. Building AI models on authentic data maintains fidelity to the natural data distribution of language and context.
2. Determine Data History
Track data provenance — where each data point comes from, when it was created, and whether it was AI-generated or human-authored. Metadata tagging and data lineage tools can help organizations identify AI-contaminated subsets within large datasets.
3. Leverage Data Accumulation
Continually collect new, original data points from user interactions, surveys, and updated sources. Over time, this creates a dynamic and expanding dataset that offsets synthetic content drift and ensures training datasets remain aligned with the real-world environment.
4. Use High-Quality Synthetic Data
Not all synthetic data is harmful. When properly generated and validated, high-quality synthetic data can augment limited real-world data — especially in domains like healthcare or cybersecurity, where privacy constraints limit access.
The key is using controlled generation, ensuring that synthetic examples are derived from accurate, domain-specific information rather than model outputs from uncontrolled web scraping.
5. Implement AI Governance Tools
Modern AI governance platforms provide organizations with the ability to monitor, validate, and control data flows into model training pipelines. These tools can:
- Identify synthetic or duplicate data within training sets.
- Enforce data quality thresholds.
- Log all data sources and changes.
- Apply bias and accuracy checks before retraining.
Governance systems act as the firewall between raw data and model ingestion, ensuring that future models remain resilient and explainable.
How Does AI Model Collapse Relate to Other Model Degradation Issues?
AI model collapse is part of a broader family of model degradation challenges in machine learning and artificial intelligence. It shares conceptual overlap with:
- Catastrophic forgetting: When models lose previously learned knowledge during fine-tuning or continual learning.
- Data drift: When the statistical properties of input data change over time, reducing predictive accuracy.
- Concept drift: When the relationship between input features and outputs shifts due to evolving real-world conditions.
- Overfitting: When a model becomes overly specialized to training data and fails to generalize to unseen examples.
However, model collapse is unique because it arises not from real-world changes but from recursive contamination — AI models learning from their own outputs rather than reality. This risk is magnified in the generative AI (GenAI) era, where synthetic content circulates rapidly across public datasets, search indexes, and digital platforms.
If unchecked, the accumulation of AI-generated data across the internet may jeopardize the integrity of next-generation models, from small domain-specific tools to massive foundation models developed by companies like OpenAI and Anthropic.
Conclusion
AI model collapse represents one of the most critical data challenges in the age of generative artificial intelligence. As large language models and foundation models continue to power the world’s digital infrastructure, ensuring access to high-quality, human-generated, and traceable training data becomes essential to maintaining performance, safety, and trust.
By adopting rigorous AI governance, diversifying data sources, and maintaining transparency throughout the AI development lifecycle, organizations can safeguard their AI systems against collapse — preserving innovation while protecting the integrity of artificial intelligence itself.
About WitnessAI
WitnessAI is the confidence layer for enterprise AI, providing the unified platform to observe, control, and protect all AI activity. We govern your entire workforce, human employees and AI agents alike, with network-level visibility and intent-based controls. We deliver runtime security for models, applications, and agents. Our single-tenant architecture ensures data sovereignty and compliance. Learn more at witness.ai.
