What is AI Governance?
AI governance refers to the frameworks, policies, and safeguards established to ensure the responsible use of AI technologies. It involves defining guidelines for AI systems throughout their lifecycle, from development to deployment, fostering ethical AI adoption while mitigating AI risk. Effective AI governance encompasses regulatory compliance, ethical AI principles, and the implementation of governance structures that ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI applications.
AI governance also plays a key role in fostering trust in AI technologies, ensuring that organizations can adopt AI responsibly without compromising human rights, data privacy, or ethical standards. As AI applications become more advanced, AI governance frameworks must evolve to address emerging risks, including those posed by generative AI and large language models (LLMs).
Why is AI Governance Needed?
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has led to its widespread adoption across sectors, including healthcare, finance, and the private sector. However, the impact of AI raises concerns related to data privacy, decision-making biases, explainability, and AI safety. The governance of AI is crucial to:
- Ensure AI ethics and compliance with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and the EU AI Act.
- Establish trust among stakeholders, including policymakers, businesses, and consumers.
- Minimize risks associated with AI models and algorithms.
- Promote responsible AI governance through AI risk management frameworks.
- Safeguard human rights and ensure equitable AI applications.
- Encourage AI adoption in a way that prioritizes safety and accountability.
- Ensure AI development aligns with ethical guidelines and industry-specific regulations.
Without a strong governance framework, organizations risk deploying AI technologies that may unintentionally cause harm, leading to regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and loss of public trust. AI governance structures provide a roadmap for responsible AI use, helping organizations balance innovation with risk management.
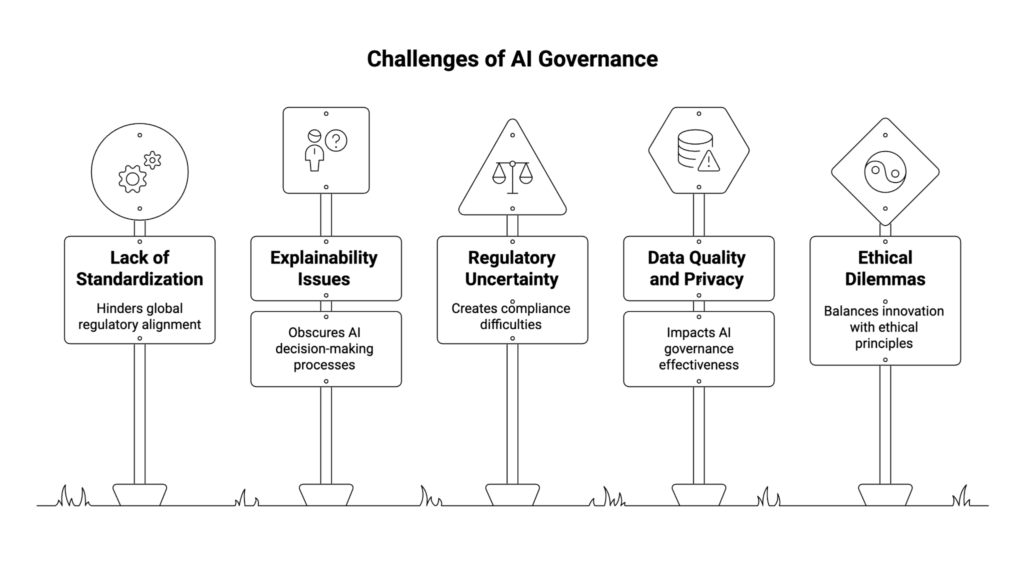
What are the Challenges with AI Governance?
Despite its necessity, AI governance faces several challenges:
- Lack of Standardization: AI governance frameworks vary across regions, making global alignment difficult.
- Explainability Issues: Many AI tools and machine learning models function as black boxes, making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: AI regulation is still evolving, with different frameworks emerging in different jurisdictions.
- Data Quality and Privacy Concerns: The effectiveness of AI governance depends on high-quality data and compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Balancing innovation with ethical AI principles remains complex, especially in high-stakes AI use cases.
- AI Risk Management Complexity: Governance must address algorithmic bias, unintended consequences, and decision-making errors.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Effective governance requires collaboration among governments, corporations, researchers, and civil society.
What is the Difference Between IT Governance and AI Governance?
While IT governance focuses on managing and securing information technology infrastructure, AI governance specifically addresses the unique challenges of AI development and deployment. Key differences include:
- Decision-Making Complexity: AI models rely on autonomous decision-making, requiring additional safeguards.
- Risk Assessment: AI risk assessment must account for algorithmic bias, explainability, and fairness.
- Lifespan and Learning: Unlike traditional IT systems, AI systems evolve over time, necessitating continuous monitoring and updates.
- Regulatory Focus: AI governance emphasizes compliance with AI-specific regulations, including fairness metrics and ethical guidelines, whereas IT governance focuses primarily on cybersecurity and data management.
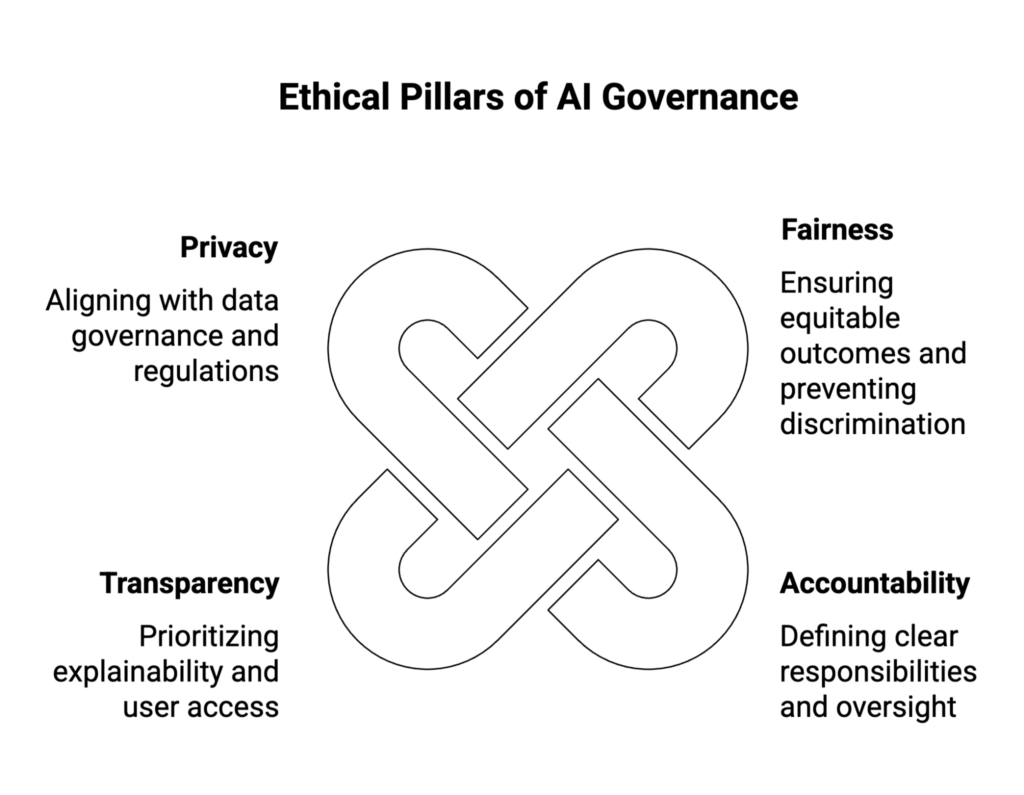
Ethics’ Role in AI Governance
Ethical AI is a fundamental component of responsible AI governance, ensuring AI systems align with human rights and societal values. Ethical guidelines emphasize:
- Fairness
- Prevent discrimination and ensure equitable outcomes.
- Use fairness metrics to measure bias in AI models.
- Train AI on diverse datasets to avoid perpetuating societal bias.
- Accountability
- Define clear accountability structures for AI outputs.
- Assign stakeholder responsibility for AI risk management.
- Establish oversight mechanisms to monitor decision-making.
- Transparency
- Prioritize explainability and responsible use of AI.
- Ensure AI tools provide reasoning for their decisions.
- Give users access to information about how AI impacts them.
- Privacy
- Align with data governance policies and global regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Minimize data collection and implement safeguards such as encryption.
Learn More: The Growing Importance of AI Ethics in the Age of Intelligent Systems
How Can AI Governance Help Mitigate Biases in AI Systems?
Bias in AI systems can result in unfair outcomes and discrimination, particularly in areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement. AI governance frameworks mitigate bias by:
- Implementing fairness metrics to evaluate model outputs.
- Training on diverse and representative datasets.
- Conducting regular bias audits.
- Establishing human oversight in high-stakes decisions.
- Regulating automated decisions in critical applications.
- Designing systems with transparency and explainability.
- Embedding feedback loops for continuous monitoring and improvement.
What is a Governance Framework?
An AI governance framework is a structured approach that guides organizations in managing risk, ensuring ethical AI, and complying with AI policies. Examples include:
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework – Structured approach for identifying and mitigating AI risks.
- OECD AI Principles – Global guidelines for trustworthy AI.
- Microsoft and IBM AI Governance Initiatives – Enterprise efforts for responsible AI development.
- EU AI Act – Regulatory structure for AI compliance across the European Union.
- ISO AI Governance Standards – Global standards for AI safety and compliance.
Learn More: AI Governance Frameworks: Building Responsible and Compliant AI Systems
How Can AI Governance Frameworks Ensure Ethical AI Development?
AI governance frameworks serve as structured blueprints for embedding ethics into every stage of the AI lifecycle—design, training, deployment, monitoring, and retirement. They provide a set of repeatable processes that ensure organizations do not simply react to ethical risks, but proactively design safeguards. Ethical development under these frameworks includes several core practices:
- Embedding Ethics from the Start
Instead of treating fairness and privacy as afterthoughts, frameworks ensure that ethical considerations are integrated during the design and data collection phases. For example, fairness criteria can be included in dataset selection, labeling practices, and feature engineering. - Formalizing Risk Assessment and AI Safety
Governance frameworks require structured evaluations of risk, including adversarial vulnerabilities, data quality issues, and model drift. Ethical AI development means assessing not only technical robustness but also social impact—e.g., whether predictive models reinforce historical inequities. - Ensuring Multi-Stakeholder Input
Ethical AI cannot be defined by technologists alone. Frameworks encourage participation from compliance officers, ethicists, domain experts, and even external civil society groups. This ensures policies align with societal values and not just business goals. - Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops
Since AI systems learn and evolve, governance frameworks prescribe post-deployment monitoring for bias, fairness, and safety. Ethical standards are upheld by establishing feedback mechanisms that allow stakeholders to flag unintended consequences or harmful outputs. - Regulatory and Standards Alignment
Governance frameworks translate broad ethical principles into actionable requirements that align with regulations (e.g., EU AI Act) and international standards (e.g., ISO/IEC AI governance standards). This provides a foundation for legal defensibility and organizational accountability. - Case-Based Evaluation
Many frameworks encourage scenario testing and red-teaming exercises where AI models are intentionally stress-tested. This process exposes ethical blind spots—such as discriminatory outcomes or unsafe recommendations—before deployment at scale.
By embedding these practices, AI governance frameworks act as guardrails, ensuring organizations do not only innovate quickly but also responsibly. They create an operational bridge between ethical AI principles (fairness, transparency, accountability) and day-to-day engineering practices.
What is an AI Policy?
An AI policy is a set of organizational rules and guidelines that define how AI technologies can and cannot be used. AI policies are critical for aligning enterprise AI use with governance objectives. They generally include:
- Usage Boundaries: Defining approved and prohibited use cases.
- Data Handling Rules: Outlining how sensitive data can be processed by AI systems.
- Risk Mitigation Protocols: Procedures for handling bias, errors, or misuse.
- Employee Guidance: Instructions for safe and ethical use of AI tools.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring alignment with GDPR, EU AI Act, and sector-specific rules.
AI policies function as the “operational layer” of AI governance—turning principles and frameworks into enforceable practices.
Learn More: AI Policy: Building a Framework for Responsible Artificial Intelligence Use
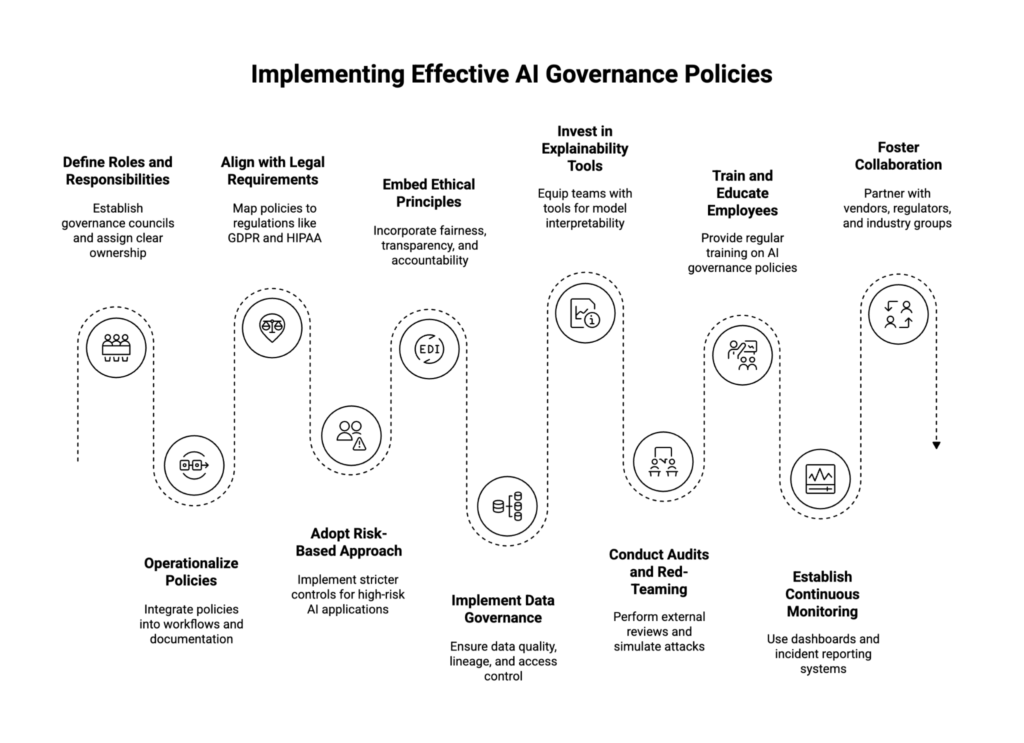
Best Practices for Implementing Effective AI Governance Policies
Building an effective AI governance program requires more than a written policy—it requires operational execution across people, processes, and technology. Below are best practices organizations can follow to strengthen their governance posture:
- Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Establish governance councils or AI oversight boards that include representatives from compliance, legal, IT, data science, and business leadership. Assign clear ownership of governance decisions so accountability is distributed and enforceable. - Operationalize AI Policies into Workflows
Policies should not sit in static documents. They must be integrated into machine learning pipelines, model documentation processes, and data governance workflows. For example, model approval checklists can enforce fairness audits before deployment. - Align with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
AI governance policies must be mapped to current and emerging regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and the EU AI Act. For multinational organizations, harmonizing compliance across jurisdictions is critical to avoid regulatory conflicts. - Adopt a Risk-Based Approach
Not all AI applications carry equal risk. A chatbot for customer support may require lighter oversight compared to an AI system that influences healthcare decisions. Best practices emphasize proportionality—higher-risk use cases should undergo stricter controls, monitoring, and human-in-the-loop mechanisms. - Embed Ethical AI Principles
Incorporate fairness, transparency, and accountability into every policy. This includes mandating bias testing, requiring explainability for critical decision-making, and implementing user rights such as appeal or override mechanisms. - Implement Strong Data Governance
Since data is the foundation of AI, robust governance must extend to data quality, lineage, and access control. Policies should define standards for anonymization, encryption, and secure sharing of sensitive datasets. - Invest in Explainability and Transparency Tools
Equip teams with model interpretability methods such as SHAP or LIME, and ensure outputs are documented in ways understandable to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Transparency improves trust and enables regulatory defense. - Conduct Independent Audits and Red-Teaming
External reviews by auditors, researchers, or regulators provide credibility to governance claims. Red-teaming exercises can simulate adversarial attacks or misuse scenarios to test the resilience of governance controls. - Train and Educate Employees
AI governance policies only succeed when employees understand them. Regular training programs ensure staff—from data scientists to business managers—know how to identify risks, follow policies, and escalate issues when needed. - Establish Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
AI governance must be a living process. Organizations should use monitoring dashboards, incident reporting systems, and regular policy reviews to adapt governance as AI models evolve, new risks emerge, or regulations change. - Foster Collaboration Across Stakeholders
Governance is most effective when aligned across the ecosystem. Partnering with vendors, regulators, and industry consortiums helps ensure shared standards and prevents siloed or inconsistent governance practices.
By adopting these best practices, organizations can move beyond compliance checkboxes and create governance programs that both protect against risk and accelerate innovation. Effective AI governance is not about slowing down progress—it’s about enabling sustainable, trustworthy AI adoption at scale.
What is an AI Governance Platform?
An AI governance platform is a dedicated software solution that helps organizations implement governance policies, monitor AI systems, and ensure compliance with regulations. These platforms typically provide:
- Visibility: Monitoring how AI is being used across an enterprise.
- Policy Enforcement: Applying rules to ensure AI aligns with company standards and regulations.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks such as bias, data leakage, or non-compliance.
- Auditability: Maintaining logs and evidence of AI system decisions for accountability.
- Integration: Connecting with LLMs, machine learning pipelines, and enterprise applications.
By centralizing oversight, AI governance platforms enable enterprises to scale AI responsibly while reducing operational and compliance risks.
Learn More: AI Governance Platforms: Empowering Responsible AI Adoption at Scale
About WitnessAI
WitnessAI is the confidence layer for enterprise AI, providing the unified platform to observe, control, and protect all AI activity. We govern your entire workforce, human employees and AI agents alike, with network-level visibility and intent-based controls. We deliver runtime security for models, applications, and agents. Our single-tenant architecture ensures data sovereignty and compliance. Learn more at witness.ai.
Related Content:
- AI Governance Frameworks: Building Responsible and Compliant AI Systems
- AI Governance Platforms: Empowering Responsible AI Adoption at Scale
- AI Policy: Building a Framework for Responsible Artificial Intelligence Use
- AI Policy Template: A Guide for Responsible Use of AI in Organizations
- LLM Observability: A Complete Guide to Monitoring Large Language Models
- AI Alignment: Ensuring AI Systems Reflect Human Values
- Model Governance: Managing Risk, Compliance, and AI Performance
- The Growing Importance of AI Ethics in the Age of Intelligent Systems
- AI Regulations Around the World: Laws, Challenges, and Compliance Strategies
