What is Shadow AI?
Shadow AI refers to the unsanctioned or unauthorized use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools, applications, or models within an organization—without the knowledge or approval of the IT department or governance bodies. This includes employees using generative AI tools like ChatGPT, OpenAI APIs, or other AI-driven platforms to automate tasks, generate content, or support decision-making without aligning with corporate policies or security protocols.
As AI adoption accelerates, particularly with the rise of large language models (LLMs) and accessible generative AI solutions, shadow AI is becoming a growing concern. These unauthorized AI applications often operate outside formal governance frameworks, making them difficult to track, assess, or secure.
How is Shadow AI Different from Shadow IT?
To fully understand the concept of shadow AI, it’s important to distinguish it from shadow IT—an older but closely related phenomenon.
Shadow IT
Shadow IT occurs when employees deploy unapproved software, hardware, or cloud services—such as personal SaaS tools or file-sharing platforms—without the involvement of the IT department. While often intended to streamline workflows or fill operational gaps, shadow IT introduces significant risks by bypassing established IT safeguards.
Shadow AI
Shadow AI, a subset of shadow IT, specifically involves the use of AI technologies, including generative AI tools, chatbots, or machine learning models, outside formal oversight. This includes employees inputting sensitive data into ChatGPT, using unvetted AI apps for decision support, or deploying external AI services for business automation without IT approval. The key difference lies in the complexity and opacity of AI outputs, which often involve non-deterministic logic and introduce new types of risk beyond traditional software usage.
How Does Shadow AI Occur?
Shadow AI typically emerges in environments where AI enthusiasm outpaces oversight. Employees may turn to AI solutions for productivity gains—summarizing reports, drafting emails, coding scripts, or analyzing datasets—without fully understanding the associated security or compliance risks.
Examples of Shadow AI
- A marketing analyst uses ChatGPT to generate campaign content using customer data.
- A developer integrates a third-party LLM API into a product prototype without IT review.
- An HR manager uses an AI-powered résumé screening tool not vetted by legal or compliance teams.
- A sales team employs an AI chatbot to qualify leads, storing prospect data in an unmanaged cloud environment.
These examples reflect how easily AI tools can be integrated into everyday workflows—often under the radar of IT and security teams.
What Are the Risks of Shadow AI?
While shadow AI can offer productivity benefits, it poses significant risks to organizational integrity, compliance, and cybersecurity.
Security Vulnerabilities
Unauthorized AI systems are typically not subject to internal security reviews or updates, making them vulnerable to exploits. LLMs may also introduce novel attack surfaces such as prompt injection or model manipulation, exposing the company to cybersecurity threats.
Data Loss
Shadow AI tools often rely on external servers to process data. Uploading sensitive information—customer data, financial records, or intellectual property—can lead to data leakage and breaches. Without visibility, organizations cannot ensure proper data protection or retention practices.
Regulation Violations
Using unvetted AI tools can lead to non-compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or emerging AI-specific laws like the EU AI Act. Regulatory violations can result in hefty fines and legal exposure.
Reputational Damage
In the event of a data breach, biased output, or misuse of AI-generated content, companies may suffer reputational harm. The lack of responsible AI safeguards in shadow deployments can erode trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
Why Is Shadow AI a Challenge for Organizations?
Shadow AI persists because it thrives in accessibility and convenience. Many GenAI tools require nothing more than a browser or API key—making them nearly invisible to IT monitoring.
Employees often view these tools as productivity boosters, not security risks. In decentralized or hybrid workplaces, it becomes even harder for CIOs and IT teams to maintain consistent control across endpoints, departments, and cloud environments.
Key Organizational Challenges:
- Decentralized AI usage: Employees experiment with GenAI tools outside managed environments.
- Indistinguishable outputs: AI-generated content looks human-authored, complicating audits.
- Rapid GenAI adoption: Vendors embed AI features into SaaS products faster than governance policies can adapt.
- Lack of standardized AI policies: Many companies have security policies for software—but not for AI systems and data pipelines.
The combination of these factors means even well-secured enterprises may unknowingly harbor dozens of shadow AI tools across teams, each with unique potential risks.
Can Shadow AI Impact Data Privacy?
Yes—shadow AI poses serious privacy and compliance threats by circumventing approved data governance processes.
When employees input personally identifiable information (PII), customer records, or proprietary datasets into GenAI tools, they may violate data protection laws or internal retention policies. Many free or public AI platforms store user prompts or reuse them to improve model training, creating an uncontrolled privacy risk.
Data Privacy Implications
- Loss of control over data storage and use: External AI models may retain or replicate uploaded data.
- Cross-border data transfers: AI APIs may process company data in regions lacking legal safeguards.
- Inability to audit or delete data: Once submitted to third-party AI systems, data may become unrecoverable.
- Exposure of sensitive company data: Unmanaged tools can leak trade secrets, financial details, or customer records.
For compliance teams, shadow AI effectively creates unknown data flows, breaking the chain of accountability required by modern data privacy regulations.
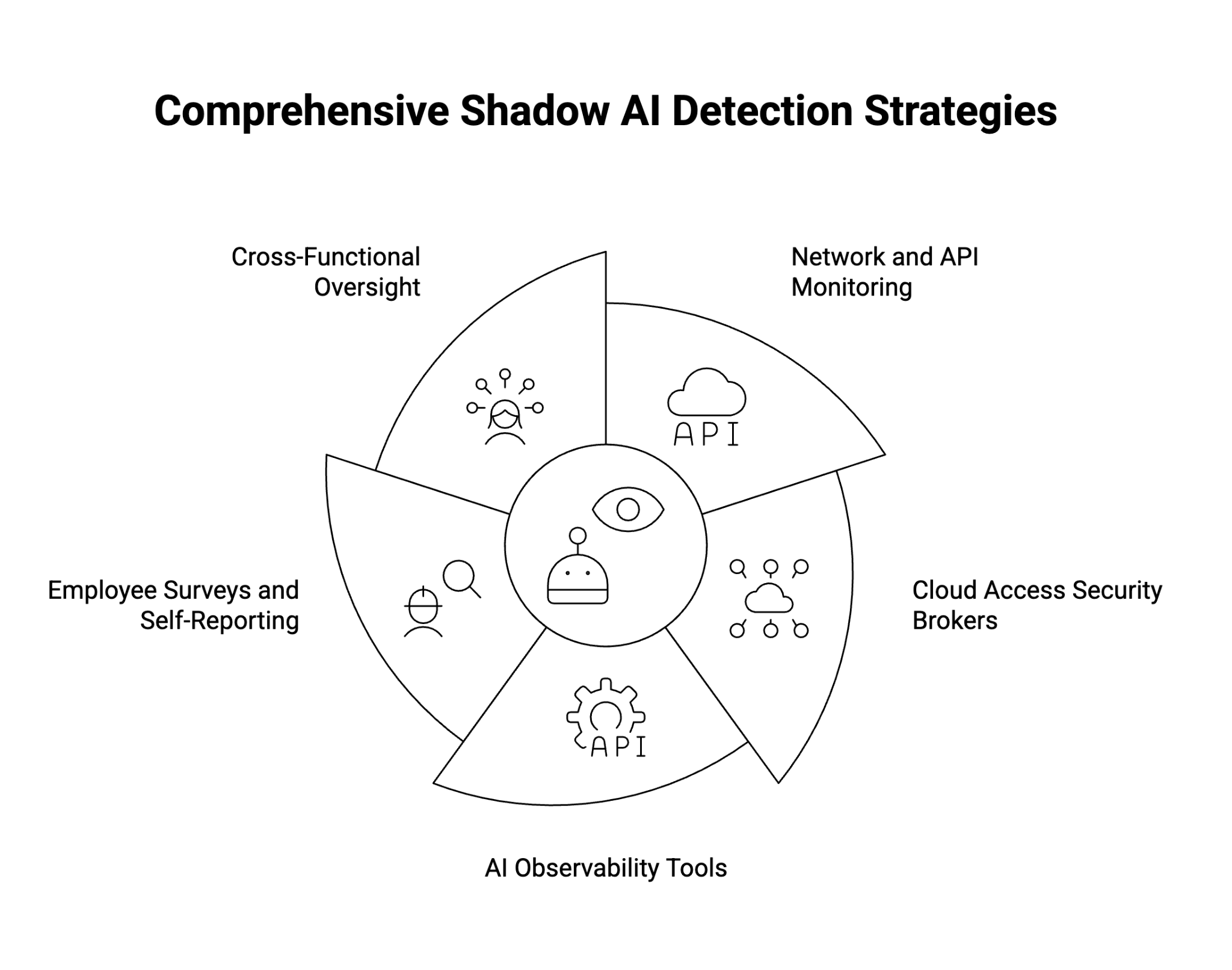
How to Detect Shadow AI
Before an organization can manage shadow AI, it must first identify where and how it’s occurring. Detection requires both technical monitoring and organizational awareness.
Detection Strategies
- Network and API Monitoring
Use traffic inspection tools or data loss prevention (DLP) systems to flag connections to known GenAI endpoints (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini). Monitoring outbound API calls helps identify unauthorized integrations. - Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB)
Deploy CASB solutions to detect SaaS and AI applications operating outside approved inventories. CASBs provide visibility into hidden data transfers and shadow workflows. - AI Observability Tools
Implement AI observability or model telemetry platforms to track how AI is being accessed and by whom. These tools can flag unusual AI usage patterns and classify GenAI interactions in real time. - Employee Surveys and Self-Reporting
Conduct internal audits or anonymous surveys to surface informal AI use cases. Many employees are willing to disclose their tools once they understand the purpose is to improve governance, not penalize usage. - Cross-Functional Oversight
Collaborate across IT, security, legal, and compliance teams to build a holistic view of AI usage. CIOs can use this data to prioritize governance initiatives and align them with enterprise AI strategies.
How to Remove Shadow AI
Once discovered, shadow AI must be systematically addressed—without discouraging innovation or creating operational bottlenecks.
Steps to Eliminate Shadow AI
- Catalog and Classify
Inventory all detected AI tools, models, and data connections. Classify them by risk level (e.g., low, moderate, high) based on the type of data processed and exposure potential. - Assess and Contain
For high-risk tools, restrict network access or disable unauthorized APIs. Containment should focus on preventing further data leakage while maintaining workflow continuity. - Replace with Approved AI Tools
Provide sanctioned, enterprise-grade GenAI alternatives that meet security and compliance standards. When employees have trusted, well-integrated options, shadow AI naturally declines. - Update AI Policies and Procedures
Establish clear approval processes for AI use cases. Define what constitutes acceptable use, acceptable data inputs, and how outputs should be reviewed and validated. - Educate and Reinforce
Train employees regularly on AI security, data privacy, and the potential risks of unvetted tools. Reinforcement from leadership—especially CIOs and department heads—helps establish a culture of responsible AI use. - Continuous Monitoring
Implement ongoing visibility programs and automated alerts for new or unauthorized AI applications. Continuous oversight ensures that shadow AI doesn’t re-emerge as the AI ecosystem evolves.
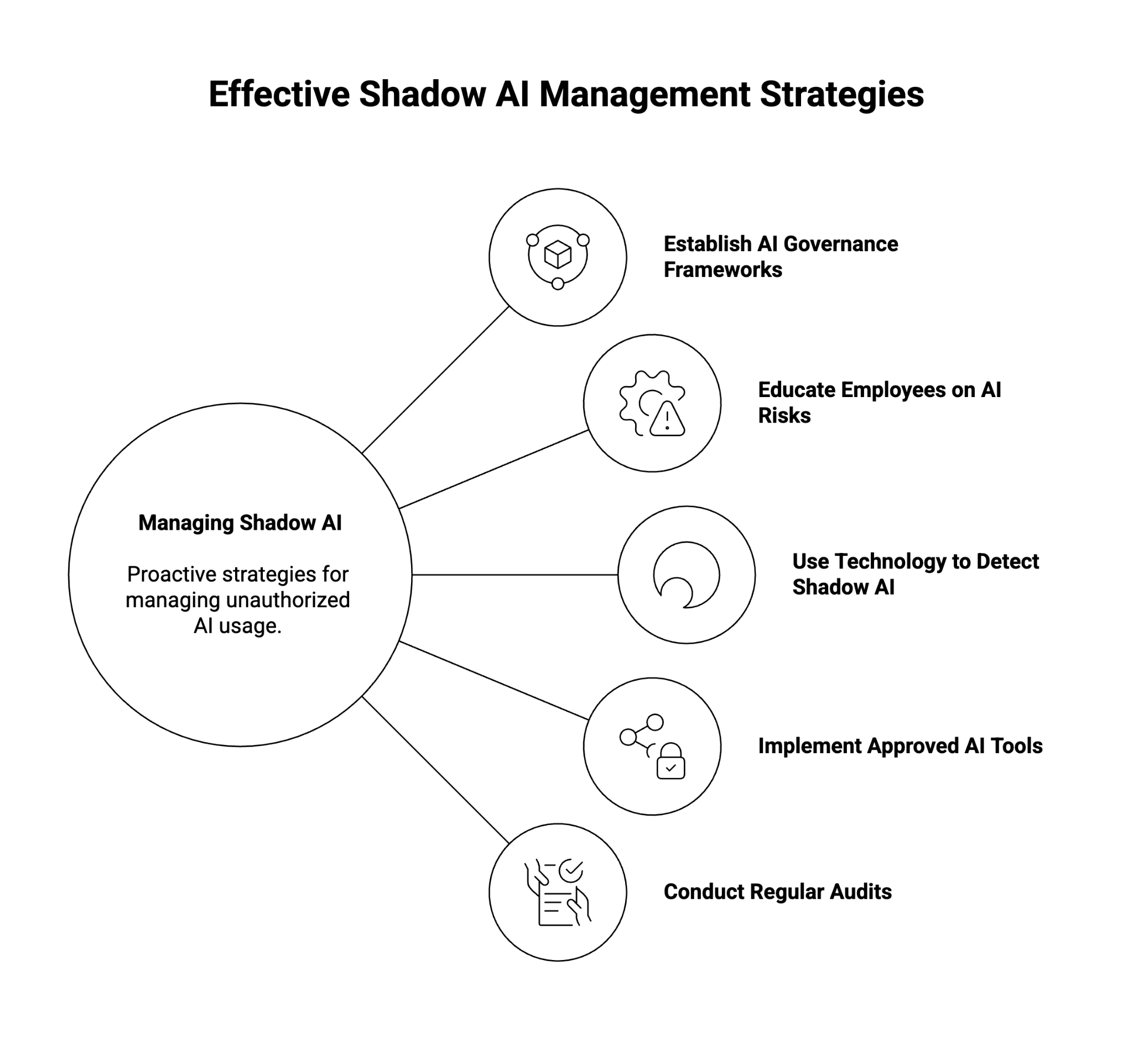
How Can Businesses Manage Shadow AI Effectively?
Proactive management of shadow AI starts with visibility, governance, and education. Organizations must balance innovation with safeguards that ensure responsible AI usage.
1. Establish AI Governance Frameworks
Create policies that clearly define acceptable AI usage, data handling rules, and approval workflows for new tools. Governance frameworks should cover both technical and ethical aspects of AI adoption, supported by oversight from IT, legal, and compliance teams.
2. Educate Employees on AI Risks
Many instances of shadow AI stem from good intentions—employees trying to streamline work or enhance productivity. Regular training can help staff understand the risks of unauthorized AI usage, including data privacy concerns, security risks, and compliance violations.
3. Use Technology to Detect Shadow AI
Employ network monitoring tools, CASBs (Cloud Access Security Brokers), and AI observability solutions to detect and flag unauthorized AI activity. Look for signs of high-volume API access, unsanctioned use of LLM platforms, or abnormal data transfers. Real-time monitoring can alert security teams to potential data leaks or compliance violations.
4. Implement Approved AI Tools
Offer employees vetted, secure alternatives that meet governance and data protection standards. When sanctioned tools are easily available and integrated into workflows, there’s less incentive for employees to seek external options.
5. Conduct Regular Audits
Review AI usage logs, conduct audits of SaaS platforms, and assess shadow AI trends within departments. These audits can identify gaps in policy adherence and help refine detection mechanisms over time.
Final Thoughts
Shadow AI is the modern evolution of shadow IT—driven by the widespread availability of powerful generative AI tools and the urgency to streamline work through automation. While the benefits of AI adoption are clear, so too are the significant risks of uncontrolled, unauthorized use. From data privacy breaches to compliance failures, shadow AI threatens the foundations of responsible AI deployment.
Enterprises must recognize shadow AI as a strategic security and governance issue. With the right mix of visibility, education, technology, and governance frameworks, organizations can harness the power of AI while protecting sensitive data, ensuring compliance, and upholding trust in AI systems.
About WitnessAI
WitnessAI is the confidence layer for enterprise AI, providing the unified platform to observe, control, and protect all AI activity. We govern your entire workforce, human employees and AI agents alike, with network-level visibility and intent-based controls. We deliver runtime security for models, applications, and agents. Our single-tenant architecture ensures data sovereignty and compliance. Learn more at witness.ai.
